On occasion, you’ve probably gotten out of bed only to realize part of your body is still asleep. It’s a weird feeling, combining burning, numbness, pain, tingling and weakness. But what if those altered sensations, called dysesthesias, were chronic? An estimated 20 million Americans—that’s 6% of the U.S. population—suffer from neuropathy, or nerve damage. The leading cause is diabetes, followed by anatomical defect, repetitive motion and Lyme disease.
Neuropathic Symptoms
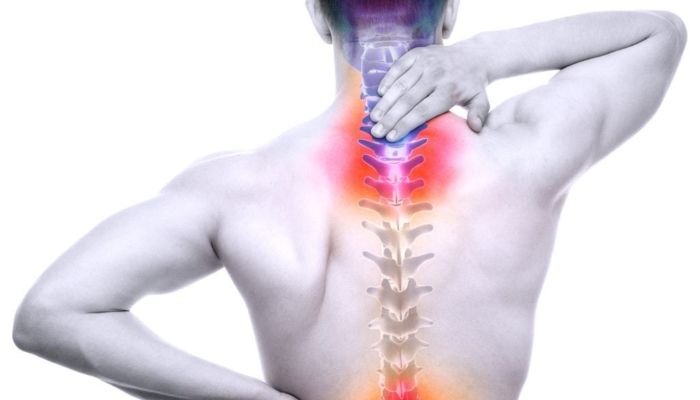
Sensory nerve compression could cause numbness, tingling or burning, which may radiate into your arms and legs. Two common examples familiar to office workers are carpal tunnel syndrome and sciatica. Carpal tunnel syndrome is the result of a pinched nerve in the wrist, and that sharp pain which starts in the lumbar region and runs down the back of one leg might mean your sciatic nerve is compressed. If there’s damage to motor neurons, the nerve cells that control muscles, you could experience weakness and even paralysis.
Diagnosing Nerve Damage
With tens of thousands of nerves in the body and neuropathic etiology ranging from aging and vitamin deficiencies to toxin exposure and infections, receiving the right diagnosis isn't easy. Treatment always goes according to the cause of the symptoms, so a thorough physical and neurologic exam by a well-trained doctor is crucial. Metabolic reasons have to be considered, and laboratory evaluations will also be employed.
EMG and NCS
First, your physician may order an imaging study, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or a computerized tomography (CT) scan, to get the full picture of your nerves’ anatomy. Diagnosis will then be determined by an electromyogram (EMG) and nerve conduction study (NCS). These diagnostic procedures assess the health of motor neurons, which transmit electrical impulses, causing muscles to contract. The electrical signals can be transmitted and detected by electrodes in the form of needles inserted into the muscle tissue or patches taped to the skin. Stimulating, recording and analyzing neuromuscular activity (EMG) and measuring the speed of conduction (NCS) can reveal the exact dysfunction.
Your Treatment Options
Not all neurologic deficits have to be treated surgically. Treatments include medications, physical therapy, and injection therapy like a nerve block, which temporarily stops the aggravated nerve from transmitting pain signals. Injection and physical therapies, in concert, are often the best way to avoid surgical intervention.
At NewSouth NeuroSpine, spine-related nerve damage is the most common presentation. Our clinic is uniquely set up to address the particular needs of these patients with the collaborative effort of physicians in physical medicine, spinal intervention and surgery. Make an appointment with a doctor at NS2 right away if you have any of the above symptoms. We’ve got your back.